Notifications
4 minutes, 10 seconds
-9 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes 0 Reviews

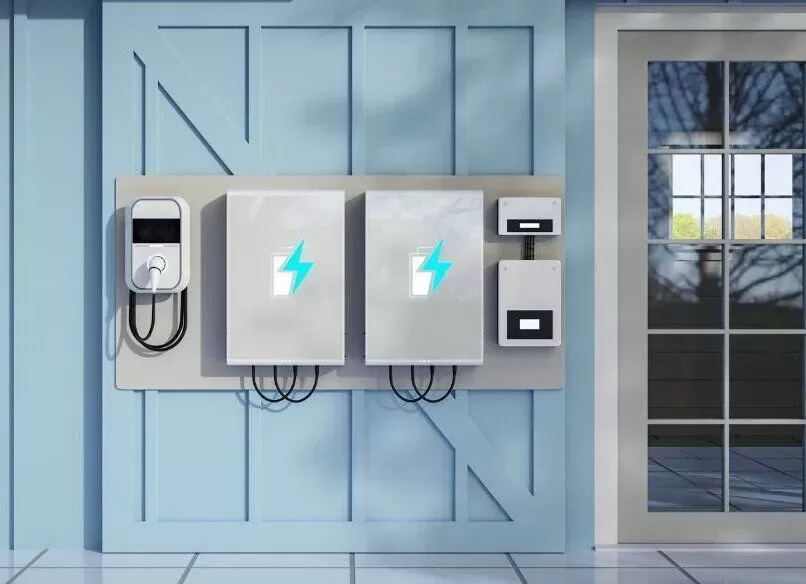
As a leading EV charger manufacturer in China, LiCB Charge offers reliable AC and DC electric vehicle charging stations, along with comprehensive charging solutions to meet diverse needs.
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to rise in popularity, so does the demand for efficient charging solutions. While DC fast chargers—known for their ability to quickly replenish EV batteries—are common in commercial and public settings, their presence in residential environments is rare. This article examines the feasibility of installing DC fast chargers at home, exploring the technical, safety, and financial challenges involved. We also highlight more practical alternatives for homeowners seeking to optimize their EV charging setup.
Consider clarifying:
“Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which use alternating current (AC) and rely on the vehicle’s onboard charger, DC fast chargers bypass this system by delivering high-voltage DC electricity directly to the battery, allowing for much faster energy transfer.”
Under “Technical Barriers”: You could mention average home voltage/amperage limits (e.g., 240V/100–200A) vs. commercial setups (>480V, 3-phase).
Under “High Installation Costs”: Consider adding a cost comparison:
"While a typical Level 2 charger installation may cost between $500 and $2,000, a DC fast charger can cost upwards of $10,000 to $50,000 when including equipment, permits, and electrical upgrades."
Excellent coverage. Just a few enhancements for clarity and readability:
You might break out the pros and cons in a small table or bullet format for Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 chargers for quicker comparison.
Rephrase for flow:
“Most homes have a 100-amp or 200-amp electrical panel. Installing a Level 2 charger typically requires a dedicated 240V circuit, often rated for 30 to 50 amps.”
Include a tip:
“Tip: A shorter cable run between the panel and charger helps reduce both material cost and energy loss.”
Add clarity to the financial section:
“In addition to upfront installation costs, many utility companies offer rebates or tax credits for residential EV chargers, which can help offset the initial expense.”
A stronger close could be:
“By planning for future needs—such as additional EVs, increased battery capacities, or integration with solar power—you can ensure that your charging infrastructure remains relevant for years to come.”
DC fast chargers have revolutionized public EV charging but remain largely impractical for home use due to their demanding infrastructure, safety requirements, and high cost. For the vast majority of homeowners, Level 2 chargers offer the best balance of speed, affordability, and convenience. By carefully evaluating your home’s electrical capacity, charging needs, and future plans, you can choose an EV charging solution that is both effective and sustainable.Know more about Google SEO Directory
China EV Chargers EV Charger Manufacturer Smart EV Chargers Electric Car Chargers Electric Vehicle Chargers Electric Car Charging Stations

