Notifications
10 minutes, 28 seconds
-70 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes 0 Reviews

As electric vehicles (EVs) gain traction globally, understanding the various types of charging connectors has become crucial for both current and prospective EV owners. Since charging connectors are not universal, it's important to know the right type based on your vehicle, charging location, and region. This article will explore the different EV charging plug types, their functionalities, and compatibility, ensuring you can make the best choice for a seamless and efficient charging experience, whether you're at home, work, or on the road.
AC (alternating current) charging is the most common form of charging for EVs, perfect for daily charging needs. It's generally divided into two main levels: Level 1 and Level 2, which cater to different charging speeds and requirements.
Level 1 Charging: The Basic Option
Level 1 charging is the simplest and most widely accessible. Using a standard 120-volt household outlet and the cable provided with your EV, this option delivers a modest charging rate—roughly 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. While this is ideal for overnight charging or drivers with shorter commutes, it is relatively slow. For those who need faster charging, Level 2 is the better option.
Level 2 Charging: Faster and More Efficient
Level 2 charging operates at 240 volts and is much faster, providing up to 40 miles of range per hour. This level requires a dedicated charging station that can be installed at home or found at public charging stations in places like shopping centers and workplaces. Level 2 charging is widely regarded as the most balanced option for most EV owners.
In North America, two main AC charging connector standards are used:
SAE J1772: This is the standard connector for most non-Tesla EVs in North America. It supports both Level 1 and Level 2 charging and is commonly found at public charging stations.
NACS (Tesla Connector): Developed by Tesla, the NACS connector is exclusive to Tesla vehicles, though Tesla has opened its Supercharger network to other EVs, potentially expanding the use of this standard in the future.
While AC charging is sufficient for daily use, DC fast charging is the go-to option when time is of the essence. DC fast charging bypasses the vehicle’s onboard charger, delivering power directly to the battery and enabling much faster charging speeds. This method is ideal for long-distance travel or when you need a quick boost.
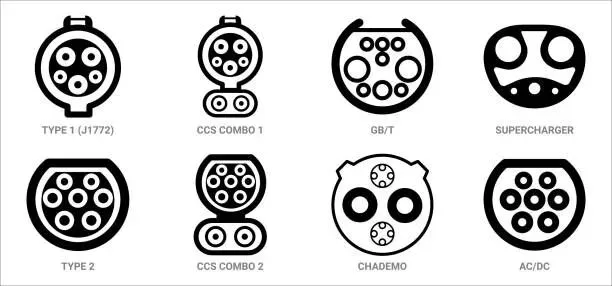
In North America, there are three main types of DC fast charging connectors: SAE Combo (CCS1), CHAdeMO, and NACS. Each offers different features and levels of compatibility.
SAE Combo (CCS1): The Combined Charging System (CCS) connector combines both AC and DC capabilities. CCS1, used in North America, builds on the SAE J1772 connector, adding two extra DC pins. This connector supports charging rates of up to 350 kW, making it one of the fastest charging options available.
CHAdeMO: Developed in Japan, CHAdeMO is another DC fast charging standard. While its use has decreased with the rise of CCS, it remains the standard for certain older EV models, especially from Japanese manufacturers.
NACS (Tesla Connector): Tesla’s NACS connector is unique in that it supports both AC and DC fast charging. Though primarily used by Tesla vehicles, the company’s decision to open its network to other EVs could lead to broader adoption.
As EV technology advances, higher power DC chargers are becoming more common. Chargers with power outputs of 150 kW, 270 kW, and even 350 kW are becoming more prevalent. These chargers can rapidly add hundreds of miles of range in just minutes, making them perfect for long journeys.
The Combined Charging System (CCS) has emerged as the global leader in DC fast charging. Its robust design and high-power capabilities make it the preferred choice for automakers and charging infrastructure operators.
CCS Type 1 and Type 2:
CCS Type 1: Primarily used in North America, this version of CCS is based on the SAE J1772 connector and includes two additional DC pins for fast charging.
CCS Type 2: Used in Europe, CCS Type 2 is based on the Mennekes Type 2 connector and includes similar DC pins for fast charging.
Advantages of CCS: CCS connectors are versatile, supporting both AC and DC charging through a single plug. This streamlines the charging experience and reduces the need for multiple connectors. Additionally, CCS can support up to 350 kW of power, making it suitable for modern high-speed chargers.
Challenges and Compatibility: CCS connectors are incompatible with CHAdeMO or GB/T systems, which use different communication protocols. Adapters are available but may not offer the same seamless experience as native connectors.
CHAdeMO, developed by a consortium of Japanese companies, was one of the first DC fast charging standards. Though it's now less commonly used due to the widespread adoption of CCS, it still plays an important role, particularly for older EVs, especially from Japanese manufacturers.
Key Features of CHAdeMO:
Bidirectional Charging: CHAdeMO supports bidirectional charging, which means that EVs can not only charge but also send power back to the grid or supply power to a home.
Compatibility: CHAdeMO is not compatible with CCS or GB/T connectors, limiting its usage in regions where these standards are predominant.
The Future of CHAdeMO: While its dominance has waned, CHAdeMO remains important for certain vehicles and offers unique features, like bidirectional charging, that could ensure its place in niche applications.
In China, the GB/T standard is the dominant charging connector for both AC and DC charging. Developed by the Chinese government, it is used by most Chinese-made EVs.
Key Features of GB/T:
AC and DC Charging: Like CCS, GB/T supports both AC and DC charging, offering flexibility for EV owners.
High-Power Capabilities: GB/T connectors can handle up to 250 kW of power, making them suitable for rapid charging applications.
Global Impact of GB/T: While primarily used in China, the influence of GB/T is growing as Chinese automakers expand globally. However, its incompatibility with CCS and CHAdeMO may hinder its adoption outside China.
Tesla’s North American Charging Standard (NACS) is a proprietary connector used mainly for Tesla vehicles. However, the company has announced plans to open its network to other EVs, which may increase adoption.
Advantages of NACS:
Compact Design: NACS is smaller and more compact than other connectors like CCS or CHAdeMO, making it easier to handle and install.
High Power Capabilities: NACS can support power levels of up to 250 kW, suitable for fast charging.
Challenges and Future Prospects: While NACS is currently limited to Tesla vehicles, the expansion of the Supercharger network to other automakers may increase the connector’s adoption. However, its proprietary nature could limit its appeal outside of Tesla.
As the electric vehicle market evolves, understanding the different charging connector types is crucial for a smooth and efficient charging experience. Whether you are using AC charging for daily needs or DC fast charging for long trips, choosing the right connector can significantly improve your experience. With the growth of high-power chargers and the increasing standardization of connectors, the future of EV charging is brighter than ever. By staying informed about connector types, you'll be well-equipped to make the best charging decisions for your electric vehicle.Know more about Google SEO Directory
China EV Chargers EV Charger Manufacturer EV Charging Solutions
